•Rule node
•Overview
Adds conditional logic to workflows. Rules allow you to define conditions to determine which execution path should be taken. If conditional logic is evaluated to true the next step will be the node connected to the upper port, otherwise, the next step will be through the lower port.
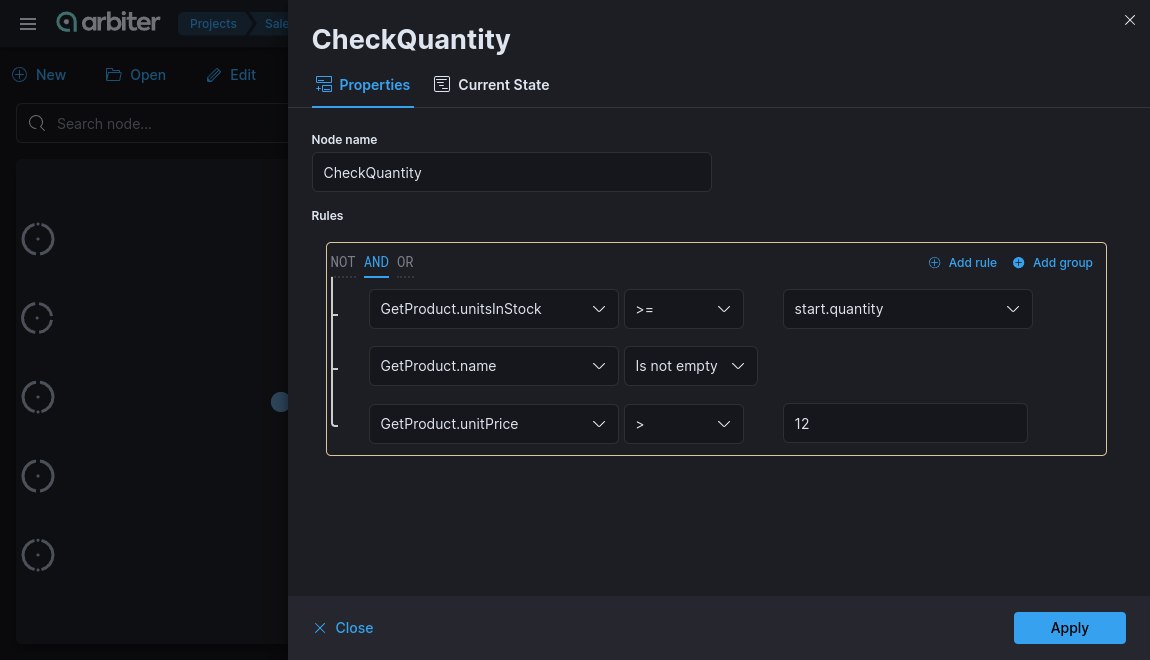
•Properties
Each rule group contains a set of rules and uses logical operators (and, or, not).
- Using the
ORoperator, we can create an expression that is true when either of two conditions are true. - Using the
ANDoperator, we can create an expression that is true only when both of the conditions are true. - Using the
NOToperator, we can reverse the truth value of an entire expression, from true to false or false to true.
Fields can be of type:
- simple (string, number, bool, date/time/datetime, list)
- structs (will be displayed in select as tree)
Based on the type of data you will see different comparison operators. Comparison operators can be:
- binary (== != < > ..)
- unary (is empty, is null)
- 'between' (for numbers, dates, times)
- complex operators like 'proximity'
Values of fields can be compared with:
- values
- another fields (of same type)
In the ‘Current State’ tab you can check the available data from previous steps.